Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Irisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki; Igarashi, Takahiro; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Abe, Hitoshi
Proceedings of European Corrosion Congress 2016 (EUROCORR 2016) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2016/09
In this study, we focused on the effect of the boiling of nitric acid solution on the corrosion of a stainless steel-made concentrator in reduced pressure in fuel reprocessing plant. In order to perform the simulation test in a non-radioactive condition, nitric acid solution with the addition of vanadium as an oxidizing metal ion were used. Corrosion tests were carried out under the conditions of boiling at reduced pressure, and of non-boiling at normal pressure and several temperatures. As a result, corrosion was accelerated by the solution boiling while it was not by non-boiling at the same temperature. It was found also that the temperature dependence of corrosion rate is the same in the both conditions of boiling and non-boiling. The corrosion accelerating effect will be discussed on the basis of the reaction among nitric acid, NOx and vanadium, etc.
Kato, Chiaki; Yano, Masaya*; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Corrosion Engineering, 52(1), p.53 - 67, 2003/01
The effects of heat-transfer on the corrosion of zirconium was examined in boiling nitric acid solutions with various concentrations. Corrosion mass losses and electrochemical polarization curves were measured on the heat-transfer and isothermal surfaces in the solutions. It was found that the corrosion rate of zirconium was higher on the heat-transfer surface than that on the isothermal surface. The rate increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition on the surface and the removal of the decomposition product from solution by boiling bubbles. The redox potential of 12 mol/dm nitric acid on a boiling heat-transfer surface was very close to the breakdown potential of primary passivity of zirconium. This suggests the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface in a nuclear fuel reprocessing.
nitric acid on a boiling heat-transfer surface was very close to the breakdown potential of primary passivity of zirconium. This suggests the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface in a nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Corrosion Engineering, 52(1), p.69 - 85, 2003/01
It is necessary to know the generation mechanism of high equilibrium potential in the solutions. Existing nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions were first analyzed by Raman spectroscopy and then existing amount of nitrogen oxides were examined by thermodynamic calculation using the SOLGASMIX software. The Raman spectroscopic analysis showed that the existing amount of un-dissociated HNO increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO
increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO , NO
, NO
 , HNO
, HNO , NO
, NO , and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO
, and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO /HNO
/HNO equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
Kato, Chiaki; Yano, Masaya*; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 52(1), p.35 - 43, 2003/01
The effects of heat-transfer on the corrosion of zirconium was examined in boiling nitric acid solutions with various concentrations. Corrosion mass losses and electrochemical polarization curves were measured on the heat-transfer and isothermal surfaces in the solutions. It was found that the corrosion rate of zirconium was higher on the heat-transfer surface than that on the isothermal surface. The rate increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition on the surface and the removal of the decomposition product from solution by boiling bubbles. The redox potential of 12 mol/dm3 nitric acid on a boiling heat-transfer surface was very close to the breakdown potential of primary passivity of zirconium. This suggests the initiation of SCC on a boiling heat-transfer surface in a nuclear fuel reprocessing.
Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Sugimoto, Katsuhisa*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 52(1), p.44 - 52, 2003/01
In order to understand corrosion of metals in nitric acid solutions, it is necessary to know the generation mechanism of high equilibrium potential in the solutions, especially under boiling conditions. The Raman spectroscopic analysis showed that the existing amount of un-dissociated HNO increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The existing amount of NO
increased with increasing nitric acid concentration and solution temperature. The existing amount of NO also increased by thermal decomposition. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO
also increased by thermal decomposition. The thermodynamic calculation showed that the important nitrogen oxides in nitric acid solutions are HNO , NO
, NO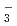 , HNO
, HNO , NO
, NO , and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO
, and NO. The equilibrium potential of nitric acid solutions is, however, mainly decided by the HNO /HNO
/HNO equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
equilibrium. The thermodynamic calculation also suggested that the increased oxidization potential on the heat-transfer surface is attributed to the reduction of nitrous acid concentration by the thermal decomposition of nitrous acid on the surface and the continuous removal of decomposition product from the solutions by boiling bubbles.
Koga, Jiro*; Shinzato, Takushi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-054, 48 Pages, 2000/02
The "STELLA" which is a tool for simulation of dynamical systems applied to the numerical simulation of the behavior of minor constituent, such as hydrazoic acid, forming and extinguishing on the operation of reprocessing process. The concentration of hydrazoic acid forming by the reaction of nitrite and hydrazine were determined by use of STELLA after the determination of concentration of main constituents by MIXSET-X. The results from simulation is shown that the STELLA is applicable to the numerical simulation of the behavior of minor constituent.
Sakurai, Tsutomu;
JAERI-Review 97-002, 62 Pages, 1997/02
no abstracts in English
 and HNO
and HNO on iodine quantity in spent-fuel solutions
on iodine quantity in spent-fuel solutionsSakurai, Tsutomu; ; ; Komaki, Yoshihide;
Nuclear Technology, 116(3), p.319 - 326, 1996/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tachimori, Shoichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 28(3), p.218 - 227, 1991/03
no abstracts in English
Tachimori, Shoichi
JAERI-M 90-018, 86 Pages, 1990/02
no abstracts in English
; *;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 13(6), p.321 - 326, 1976/06
Times Cited Count:7no abstracts in English
 -ray irradiated single crystals of sodium nitrite
-ray irradiated single crystals of sodium nitrite;
Journal of Chemical Physics, 40(5), p.1317 - 1321, 1964/00
Times Cited Count:25no abstracts in English
;
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 19(5), p.632 - 639, 1964/00
Times Cited Count:9no abstracts in English
Shimizu, Koki; Koyama, Hayato; Hagiwara, Masayoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English